Ethernet vs WiFi: Key Differences, Pros, and Best Uses
Choosing between Ethernet and WiFi is a key decision when setting up your network. While WiFi offers mobility and ease of installation, Ethernet delivers faster speeds, stronger stability, and lower latency—making it the preferred option for high-demand environments.
For businesses handling large data transfers, real-time communication, or mission-critical systems, a wired Ethernet connection is often the smarter choice. Understanding the pros and cons of Ethernet vs WiFi can help you build a network that meets your performance and reliability goals.
Understanding WiFi and Ethernet
In today's digital age, the way we connect to the internet has evolved dramatically. Understanding the fundamental differences between WiFi and Ethernet is crucial for optimizing your home network.
What is WiFi?
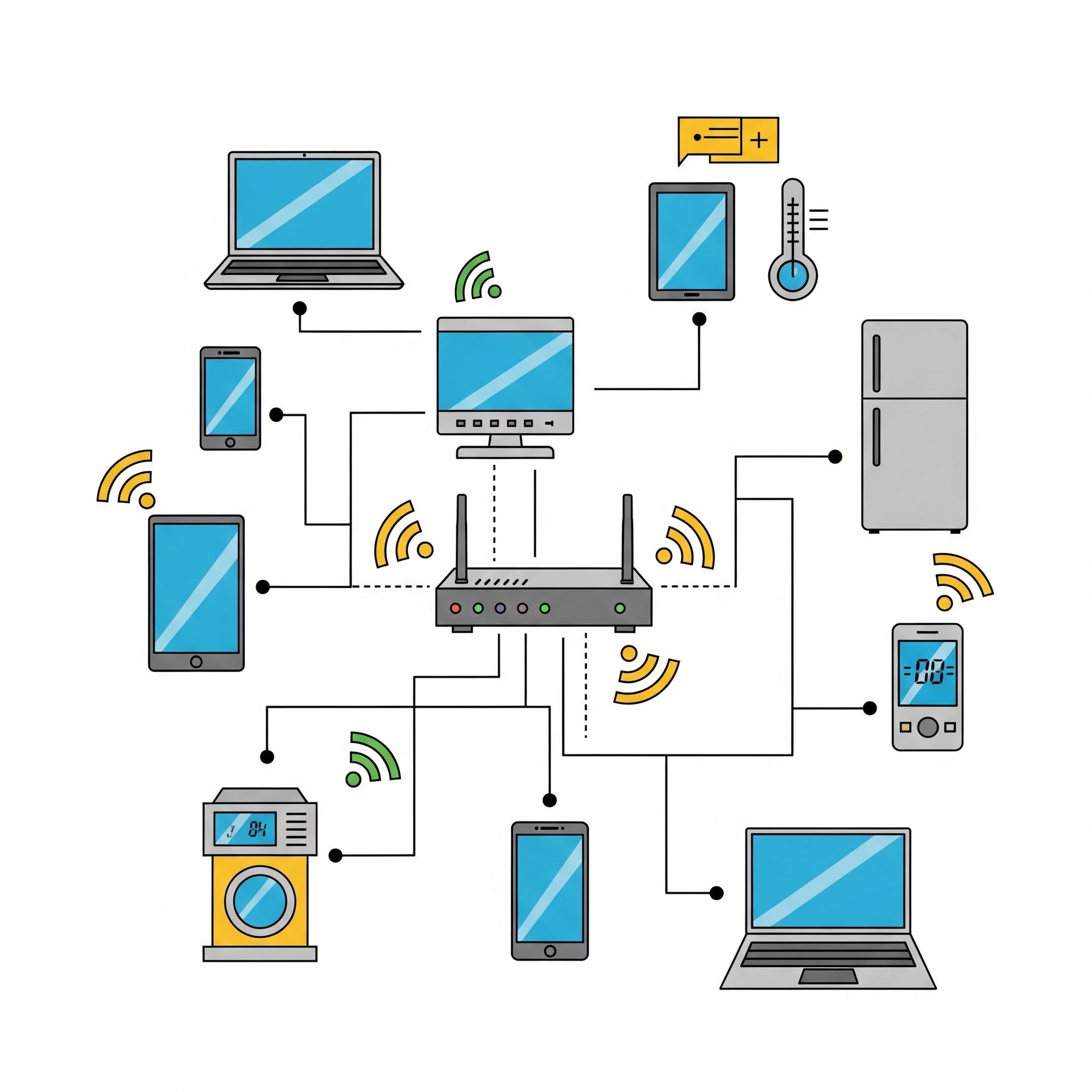
WiFi, short for Wireless Fidelity, allows devices to connect to the internet wirelessly using radio waves. It's a convenient option as it eliminates the need for physical cables, making it easy to connect multiple devices throughout your home without the clutter of wires. WiFi technology has advanced significantly over the years, with new standards like WiFi 6 offering better speeds and improved range. Despite these advances, WiFi signals can still be affected by physical obstacles and interference from other electronic devices.
WiFi networks operate on different frequency bands, primarily 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band offers a wider range but can be more prone to interference, while the 5 GHz band provides faster speeds but over a shorter range. Choosing the right frequency band can enhance your WiFi experience, depending on your specific needs and environment.
One of the main advantages of WiFi is its ability to support a wide range of devices, from smartphones and tablets to smart home gadgets. This versatility makes WiFi an attractive option for households looking for seamless connectivity across various devices.
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet, on the other hand, uses physical cables to connect devices to the internet. This wired network solution often involves the use of Ethernet cables, which are plugged into routers and devices like computers and gaming consoles. Ethernet connections are known for their reliability and stability, making them a popular choice for tasks that require a steady internet connection.
The evolution of Ethernet technology has led to the development of various cable categories, such as Cat5, Cat6, and Cat7, each offering different levels of performance. These categories determine the maximum speed and bandwidth the cable can support, with newer categories providing better performance.
Ethernet networks are typically used in environments where performance and security are priorities. Unlike WiFi, which can be susceptible to interference, Ethernet connections are less likely to experience disruptions, providing a consistent and reliable internet experience. For more about Ethernet installation and wiring, visit Cat5 Guy.
Speed: Is Ethernet Faster Than WiFi?
One of the most frequently asked questions is whether Ethernet is faster than WiFi. The short answer is: yes, generally. However, the speed comparison between the two can be influenced by various factors.
Speed of WiFi vs Ethernet
WiFi speeds can vary greatly depending on several factors such as distance from the router, interference from other devices, and the number of devices connected to the network. In ideal conditions, modern WiFi standards (like WiFi 6) can achieve impressive speeds, but real-world conditions often limit performance. Distance from the router plays a crucial role in determining WiFi speed; the further away you are, the weaker the signal strength, leading to slower speeds.
Interference from other electronic devices, such as microwaves and cordless phones, can also impact WiFi speed. Additionally, the number of devices connected to your network can affect performance, as more devices share the available bandwidth.
Ethernet connections offer more consistent and faster speeds than WiFi. With Ethernet, you can achieve speeds up to 1 Gbps (Gigabit per second) or even higher with advanced setups. This makes Ethernet the preferred choice for activities that require high-speed internet, like gaming or streaming in 4K. Ethernet connections are not affected by physical barriers or interference from other devices, ensuring a stable and fast connection.
For users who require the highest possible speeds, options like fiber optic Ethernet provide even greater performance, with speeds reaching up to 10 Gbps. This level of speed is ideal for data-intensive tasks and professional environments where network performance is critical. To learn more about Ethernet setup and services for your business, check out Cat5 Guy's Industry Data Cabling Services.
And for more services , visit our services page.
Reliability: Wired Network vs Wireless
The reliability of your network connection is a key factor to consider when choosing between WiFi and Ethernet. Each option has its strengths and weaknesses in terms of reliability.
Reliability of WiFi
WiFi is generally reliable for everyday use, but it can be susceptible to interference. Walls, other electronic devices, and even your neighbor's WiFi can affect your signal strength and reliability. The number of connected devices can also impact WiFi reliability, as more devices can strain the available bandwidth.
Environmental factors, such as the layout of your home and the materials used in its construction, can further influence WiFi reliability. Thick walls and floors can weaken WiFi signals, leading to dead zones or areas with poor connectivity.
To improve WiFi reliability, consider using a mesh network system, which uses multiple devices to extend coverage throughout your home. This can help eliminate dead zones and provide a more consistent WiFi experience.
Reliability of Ethernet
Ethernet provides a more stable and reliable connection. Since it uses physical cables, it's less prone to interference, providing a steady connection ideal for critical tasks like working from home or online gaming. Ethernet connections are not affected by environmental factors, ensuring consistent performance regardless of the layout or construction of your home.
Ethernet's reliability makes it a popular choice for businesses and individuals who require a dependable internet connection. The use of physical cables ensures that data is transmitted directly between devices, minimizing the risk of disruptions or interference. For businesses looking to implement reliable data cabling solutions, Cat5 Guy offers expert installation services.
For users who prioritize reliability, Ethernet offers peace of mind, ensuring that your internet connection remains stable and consistent, even during peak usage times.
Cost: Ethernet Cable Cost vs WiFi Setup
When considering cost, both options have different implications. It's important to weigh the initial investment against the long-term benefits to determine the best choice for your home network.
Cost of WiFi
Setting up a WiFi network involves purchasing a wireless router. While the initial cost might be higher compared to just buying cables, the convenience and flexibility often justify the expense for many homeowners. WiFi routers come in a range of prices, with more expensive models offering advanced features like improved range, faster speeds, and enhanced security.
In addition to the router, you may need to invest in range extenders or mesh systems to ensure adequate coverage throughout your home. These additional devices can increase the overall cost of a WiFi setup.
Despite the higher initial cost, the convenience of WiFi makes it a worthwhile investment for many households, especially those with multiple mobile devices and smart home gadgets.
Cost of Ethernet
Ethernet cables are generally inexpensive, but the cost can add up if you need to run cables throughout your home. Additionally, if your devices are far from the router, you might need longer or more complex installations, which can increase costs. Professional installation may be required for complex setups, adding to the overall expense.
While the initial cost of Ethernet may be lower than WiFi, the need for extensive cabling can make it a more costly option in some cases. However, the long-term benefits of reliability and performance often outweigh the initial investment for users who require a stable and fast connection.
For those who prioritize cost-effectiveness, Ethernet offers a reliable and affordable solution, especially for stationary devices that can be easily connected via cables.
Convenience and Flexibility
The convenience and flexibility of your network setup can significantly impact your internet experience. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each option can help you make the right choice.
WiFi Flexibility
WiFi offers unmatched convenience and flexibility. You can move around your house with your device without losing connectivity. For a new homeowner, this means you can enjoy internet access on your patio, in the kitchen, or from your bed without worrying about cables. WiFi's ability to support a wide range of devices makes it an ideal choice for households with multiple users and devices.
The flexibility of WiFi allows for easy expansion of your network. As you add new devices, they can be seamlessly integrated into your existing WiFi network, providing a convenient solution for growing households.
For users who value mobility and convenience, WiFi offers the freedom to stay connected wherever you are, without the constraints of physical cables.
Ethernet Limitations
Ethernet's major drawback is its lack of flexibility. You're tethered to the cable, which can be inconvenient if your home layout doesn't allow for easy cable management. However, for stationary devices like desktops or smart TVs, this isn't a significant issue. Ethernet's reliability and performance make it an ideal choice for devices that remain in a fixed location.
While Ethernet may not offer the same level of flexibility as WiFi, it provides a stable and consistent connection that can be crucial for tasks that require high-speed internet. For users who prioritize performance over flexibility, Ethernet remains a viable option.
Despite its limitations, Ethernet offers a reliable and efficient solution for users who require a dependable internet connection, especially in environments where mobility is not a priority.
Security: Router and Ethernet vs WiFi
Security is another important factor to consider when setting up your home network. Understanding the security implications of each option can help you make an informed decision.
WiFi Security
WiFi networks can be vulnerable to hacking if not properly secured. It's crucial to use strong passwords and encryption methods like WPA3 to protect your network. Regularly updating your router's firmware and changing your WiFi password can help enhance security.
In addition to encryption, consider using a guest network to keep your main network secure. This allows visitors to access the internet without compromising the security of your primary network.
For users concerned about security, implementing strong security measures can help protect your WiFi network from unauthorized access and potential threats.
Ethernet Security
Ethernet networks are inherently more secure as they require physical access to the network. This makes it harder for unauthorized users to tap into your connection. The use of physical cables ensures that data is transmitted directly between devices, minimizing the risk of interception or unauthorized access.
For users who prioritize security, Ethernet offers a reliable and secure solution, especially in environments where sensitive data is transmitted. While Ethernet may not offer the same level of convenience as WiFi, its inherent security advantages make it a preferred choice for users who require a secure and dependable connection.
In addition to its security benefits, Ethernet provides a stable and consistent connection, ensuring that your network remains secure and reliable, even during peak usage times.
Making the Right Choice
Ultimately, the choice between WiFi and Ethernet depends on your specific needs. Evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of each option can help you determine the best solution for your home network.
Choose WiFi if:
You need flexibility, have multiple mobile devices, or if the layout of your home makes running cables impractical. WiFi offers the convenience and versatility needed to support a wide range of devices, making it an ideal choice for households with diverse connectivity needs.
For users who value mobility and convenience, WiFi provides a flexible solution that allows you to stay connected wherever you are, without the constraints of physical cables.
Choose Ethernet if:
You require fast and reliable internet for tasks like gaming, streaming, or if you have stationary devices that can easily connect via cables. Ethernet offers the performance and reliability needed for data-intensive tasks, ensuring that your internet connection remains stable and consistent.
For users who prioritize performance and security, Ethernet provides a dependable solution that can support high-speed internet and secure data transmission.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between WiFi and Ethernet allows you to make informed decisions about your home network setup. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, but by evaluating your specific needs, you can choose the right option for your home. Whether you prefer the flexibility of WiFi or the reliability of Ethernet, both can provide a solid foundation for your internet needs.
Remember, a well-thought-out network setup can enhance your online experience, reduce maintenance hassles, and ensure you get the most out of your internet service. By considering the factors outlined in this article, you can make an informed decision that meets your connectivity requirements and enhances your overall internet experience.