The Basics of Low-Voltage Cabling for New Constructions
Low-voltage cabling is a critical element in modern construction projects, enabling seamless connectivity for communication and technology systems. From high-speed internet to security networks, low-voltage cabling supports the infrastructure that powers homes, offices, and institutions. Unlike high-voltage wiring used for electrical power, low-voltage cabling operates at lower currents, prioritizing safety and data transmission.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of low-voltage cabling for new constructions, covering its types, benefits, planning strategies, and installation best practices to help stakeholders create efficient and future-ready buildings.
Key Takeaways
- Low-voltage cabling supports essential systems like internet, phone, and security.
- Common cable types include Ethernet, coaxial, and fiber optic.
- Proper planning ensures scalability and adaptability for future needs.
- Low-voltage systems are safer and more energy-efficient than high-voltage wiring.
- Structured cabling improves organization and system performance.
- Professional installation ensures compliance and reliability.
Understanding Low-Voltage Cabling
Low-voltage cabling refers to wiring systems that operate at voltages below 50 volts, designed for data, voice, and signal transmission rather than power delivery. These systems are integral to technologies such as networking, telecommunications, audio-visual setups, and security systems. Unlike high-voltage wiring, which powers appliances and lighting, low-voltage cabling focuses on delivering reliable communication signals with minimal electrical risk.
The primary advantage of low-voltage cabling is its safety. Lower voltages reduce the risk of electrical shock or fire, making it ideal for environments with high human traffic, such as schools, offices, or residential buildings. Additionally, low-voltage systems are versatile, supporting a wide range of applications essential for modern connectivity.
Types of Low-Voltage Cabling
Different types of low-voltage cables serve specific purposes in new constructions. Selecting the appropriate cable type depends on the project’s requirements and intended applications.
- Ethernet Cables (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a): Used for computer networks, these cables provide reliable internet and LAN connectivity. Cat6 and Cat6a support higher speeds and bandwidth than Cat5e, ideal for data-heavy environments.
- Coaxial Cables: Commonly used for cable TV, satellite systems, and some internet connections, coaxial cables are robust and resistant to interference.
- Fiber Optic Cables: These transmit data as light pulses, offering high-speed, long-distance connectivity for advanced networks and telecommunications.
- Audio Cables: Designed for audio systems, these cables ensure clear sound transmission for home theaters, conference rooms, or public address systems.
- Security System Cables: These support surveillance cameras, alarms, and access control systems, ensuring dependable signal transmission for safety.
| Cable Type | Primary Application | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet (Cat6) | Internet and LAN | High speed, reliable |
| Coaxial | TV, internet | Interference-resistant |
| Fiber Optic | High-speed data transmission | Long-distance, high bandwidth |
| Audio Cables | Audio systems | Clear sound quality |
| Security Cables | Surveillance, alarms | Stable signal transmission |
Benefits of Low-Voltage Cabling
Low-voltage cabling provides several advantages that make it indispensable for new construction projects. These benefits enhance functionality, safety, and efficiency.
Safety
Operating at low voltages reduces the risk of electrical hazards, making these systems safer for installers and building occupants. This is particularly valuable in settings like schools or hospitals, where safety is paramount.
Energy Efficiency
Low-voltage systems consume less power, contributing to lower energy costs. Technologies like Power over Ethernet (PoE) allow devices such as IP cameras or wireless access points to receive both power and data through a single cable, reducing energy consumption and simplifying installations.
Scalability
As technology evolves, buildings must accommodate new systems and devices. Low-voltage cabling, especially structured systems, allows for easy upgrades, ensuring long-term adaptability without major renovations.
Versatility
Low-voltage cabling supports diverse applications, from high-speed internet to smart building technologies, making it a flexible solution for modern construction needs.
Planning Low-Voltage Cabling Systems
Effective planning is essential for a successful low-voltage cabling installation in new constructions. Early consideration of technology needs helps avoid costly modifications later.
Identifying System Requirements
Start by assessing the building’s intended use. For example, a commercial office may prioritize extensive Ethernet cabling for workstations, while a residential project might focus on audio-visual and security systems. Engage stakeholders to determine current and anticipated needs.
Future-Proofing
To accommodate future technologies, choose high-capacity cables like Cat6a or fiber optics. Leaving extra conduit space during construction allows for additional cables without disrupting the building structure.
Adhering to Standards
Low-voltage cabling must comply with industry standards, such as those from the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) or the National Electrical Code (NEC). Compliance ensures safety, performance, and compatibility with modern equipment.
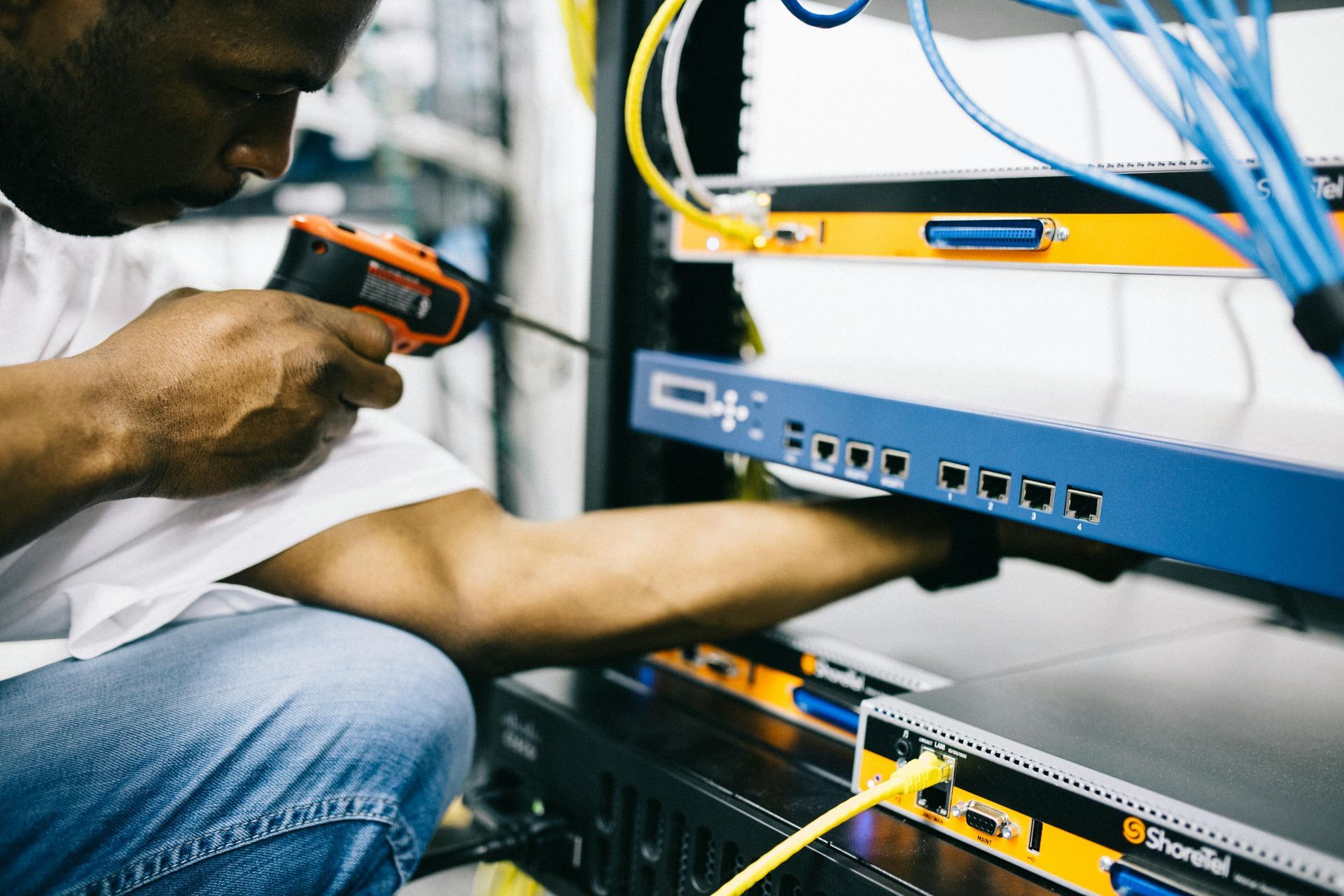
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation maximizes the performance and durability of low-voltage cabling systems. Key practices include:
- Structured Cabling: Use a standardized framework with centralized patch panels and labeled connections to simplify maintenance and scalability.
- Minimizing Interference: Keep low-voltage cables separate from high-voltage wiring to avoid electromagnetic interference, which can degrade signal quality.
- Professional Expertise: Hire certified technicians familiar with cabling standards and local codes to ensure a reliable installation.
- Testing and Validation: After installation, test all cables for connectivity and performance. Certification confirms the system meets industry standards.
Applications in New Constructions
Low-voltage cabling supports a variety of applications, enhancing the functionality of new buildings. Common uses include:
- Networking: Ethernet cables provide high-speed internet for offices, schools, and homes, supporting productivity and connectivity.
- Security Systems: Cabling connects cameras, alarms, and access controls, ensuring robust safety measures.
- Smart Building Technologies: Low-voltage systems enable IoT devices like smart thermostats and lighting, promoting automation and energy efficiency.
- Audio-Visual Systems: From conference room projectors to home theater setups, low-voltage cabling delivers high-quality audio and video.
These applications highlight the critical role of low-voltage cabling in creating technology-driven environments.
Cost Factors
The cost of low-voltage cabling depends on factors like project size, cable types, and installation complexity. While high-quality cables like fiber optics may have higher upfront costs, their durability and performance reduce long-term expenses.
To control costs, prioritize thorough planning to avoid over- or under-installing cables. Working with experienced contractors can optimize the installation process, minimizing errors and delays. Scalable systems also reduce the need for future upgrades, offering long-term savings.
Addressing Common Challenges
Low-voltage cabling installations can face challenges, but proactive solutions ensure success.
- Installation Complexity: Running cables through walls or ceilings can be labor-intensive. Solution: Use pre-planned conduits and pathways to streamline the process.
- Device Compatibility: Older equipment may not support modern cables. Solution: Verify compatibility during the planning phase.
- Budget Limitations: High-quality cabling can be costly. Solution: Balance performance and cost by selecting cables that meet both current and future needs.
Addressing these challenges early helps create a reliable and efficient cabling system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is low-voltage cabling for new constructions?
Low-voltage cabling for new constructions refers to wiring systems operating below 50 volts, used to support internet, communication, and security networks. Unlike standard electrical wiring, it’s designed for safe and efficient data transmission in modern buildings.
Why is low-voltage cabling essential in new building projects?
Low-voltage cabling for new constructions provides the foundation for reliable connectivity, powering systems like Wi-Fi, intercoms, and smart home technologies. It enhances safety, energy efficiency, and scalability, making buildings more future-ready.
What types of low-voltage cables are commonly used in new constructions?
The most common low-voltage cabling types for new constructions include Ethernet (Cat6), coaxial, fiber optic, audio, and security system cables. Each supports different functions, from high-speed internet and television to sound systems and surveillance networks.
How can builders plan and future-proof low-voltage cabling systems?
Planning low-voltage cabling for new constructions starts with identifying current and future tech needs. Using high-capacity cables like Cat6a or fiber optics and leaving conduit space ensures easy upgrades as technology evolves.
Why should you hire professionals for low-voltage cabling installation?
Professional installers ensure that low-voltage cabling for new constructions meets safety codes, reduces interference, and delivers optimal performance. Certified experts also help design scalable, organized systems that can grow with your building’s needs.
Final Thoughts
Low-voltage cabling is a foundational component of new construction projects, enabling reliable and versatile communication systems. By understanding its types, benefits, and installation best practices, builders and property owners can create spaces that are safe, efficient, and ready for future technologies.
While challenges like cost and complexity may arise, careful planning and professional installation ensure a robust system that supports modern connectivity needs. As buildings become increasingly technology-dependent, low-voltage cabling remains essential for creating connected, functional environments.
Build smarter—Plan your next project's low-voltage cabling with us.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI/TIA-568
https://www.nfpa.org/education-and-research/electrical/understanding-nfpa-70-national-electrical-code
Share this article